Causes and treatment of gums recession
Healthy gums are usually pink, with a thin edge between the tissues and your teeth. But bacteria buildup can lead to gum disease and gum recession.
At first, gum recession may go unnoticed as the gums gradually pull away from the teeth. However, if you experience increased tooth sensitivity, it may be a sign that you must go to your dentist for a checkup.
As gum recession progresses, your teeth may look longer, and the roots of your teeth may be exposed. If this happens, it’s important to act on the signs and symptoms to prevent damage to your teeth and gums. Your dentist may also notice signs of gum recession before you know it.
What are the causes of gum recession?
It can be a bit worrying at first if you notice signs of trouble with your gums. For this reason, dentists are often asked about what makes gum recession happen and how to stop it.
A common cause of receding gums is incorrect brushing protocol (brushing your teeth aggressively and incorrectly).
Other factors leading to receding gums include genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, smoking, grinding teeth, or misaligned teeth.
The causes of receding gums vary, but knowing some of the most common reasons for its development can help you avoid it and maintain healthy, firm gums.
In the long term, poor oral hygiene can lead to periodontal disease and tooth loss.
Likewise, the buildup of plaque that hardens into tartar can lead to gum recession.
Signs and Symptoms of Receding Gums
Symptoms of receding gums can appear gradually, but spotting some common signs early on can help you manage this condition.
Teeth appearing longer/bigger:
A telltale sign of early receding gums is teeth appearing longer.
Swollen/bleeding gums:
Other signs and symptoms of receding gums include bleeding after brushing, red, swollen gums, and bad breath.
Increased tooth sensitivity:
When gum line recession becomes more severe, it is common to see exposed tooth roots. Exposed roots are multifactorial and often accompanied by extreme tenderness. This condition can often be caused or aggravated by aggressive or incorrect brushing with a hard-bristled toothbrush head or other dental issues.
Loose teeth:
If the bacteria is not cleaned under the gums, over time, this can lead to inflammation or receding gums. In addition, pockets may develop under the gums, and you may notice your teeth loosening. These are signs of gum (periodontal) disease that will worsen if not treated by a dentist.
Treatment of gum recession
The right treatment for receding gums varies depending on when you notice the signs. A common gum recession treatment is deep cleaning (scaling and root planing). This deep tissue cleaning involves cleaning bacteria and tartar that may have deposited under the gums, especially between the teeth. A dentist or a periodontist can perform this treatment.
Alternatively, if you have developed more severe symptoms, treatment for receding gums may require surgery.
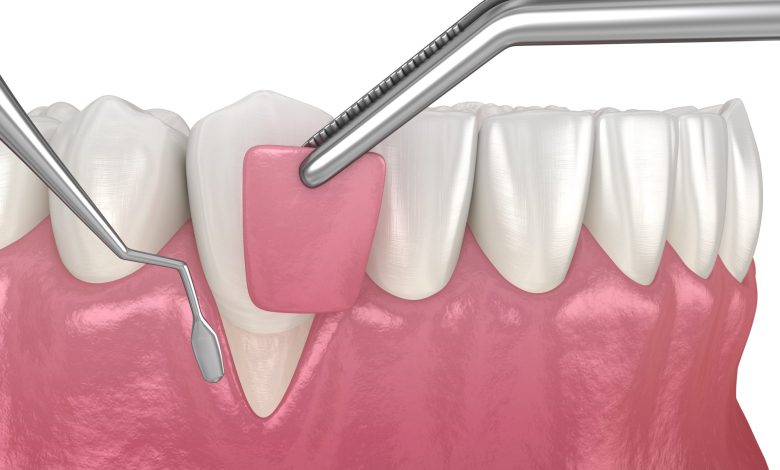
One of the most common treatments is a gum graft performed by a gum specialist (periodontist). This gum recession treatment aims to revitalize the underlying gum tissue or bone and may require the placement of bone or synthetic membrane to promote gum regeneration.
Prevention of gum recession
When it comes to learning how to prevent receding gums, there are easily preventable causes. The easiest way is to brush your teeth with a softer toothbrush, avoid applying too much pressure, and don’t use a back-and-forth brushing motion.
Regular checking by your dentist can also help spot early signs and prevent gum recession by gently cleaning away any plaque and tartar buildup. This type of cleaning is recommended twice a year to complement your daily dental hygiene routine.
Some other tips for preventing gum recession that your dentist can give you include quitting smoking, eating a balanced diet without excessive amounts of sugar, and flossing regularly.
The best way to maintain long-term healthy gums is a dental hygiene routine of brushing your teeth twice daily, rinsing your mouth with mouthwash, and flossing.
An electric toothbrush with a small round head and a built-in pressure sensor will ensure a safe and effective brushing experience.
Following these steps is a good way to prevent gum recession and reduce the risk of needing gum surgery.
Can recession-affected gums grow back?
Unfortunately, unlike other tissue types, such as skin, your gum tissue does not grow back. It is, therefore, particularly important to pay attention to the early signs of severe gum recession.
How to stop the progression of gum recession?
Suppose you’re wondering how to stop receding gums. In that case, the best steps are regular dental checkups and a systematic routine of brushing your teeth twice daily, flossing and using products recommended by dental professionals, such as antibacterial mouthwashes and antibacterial toothpaste such as toothpaste containing stannous fluoride.
How to treat gum recession?
If you notice the first signs of receding gums, your dentist will start by diagnosing the cause(s). Treatment options depend on the diagnosis and the severity of the recession. The patient’s home care and good oral hygiene instructions are integral to the treatment.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession:
Scaling and Root Planing:
Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical process that a dentist or dental hygienist does to remove plaque and tartar from tooth and root surfaces. This helps to control gum disease and prevent further gum recession.
Gum Grafting:
A gum grafting surgical treatment involves removing gum tissue from another area of the mouth, such as the palate, and transplanting it to the exposed root surfaces. This can help to restore gum tissue and reduce tooth sensitivity.
Pinhole Surgical Technique:
Using specialized devices, the gum tissue is gently repositioned over the exposed roots using the pinhole surgical technique, which is a less invasive treatment. This technique does not require grafting and has a faster recovery time compared to traditional gum grafting.
Good Oral Hygiene:
It is possible to stop future gum recession and improve gum health by developing healthy dental hygiene routines such as brushing and flossing the teeth on a consistent basis, using a toothbrush with soft bristles, and refraining from vigorous brushing.
Conclusion:
While recession-affected gums do not naturally grow back, several treatment options are available to manage gum recession and restore gum health. To prevent further complications and maintain good oral health, it is important to seek professional dental care if you are experiencing gum recession. Consulting with a qualified dentist or periodontist can help determine the best treatment option for your specific condition. Remember, early intervention and good oral hygiene are key to preventing gum recession and maintaining a healthy smile.